Buffalo is best known for its snowstorms but this story deals with an epic weather event, one that inflicted catastrophic damage on the city and it changed the lives of many forever and ended the lives for some.
Buffalo was a rapidly growing city back in the 1840s. It was the ending point for the Erie Canal, which had been constructed in the 1820s. The Great Lakes became essential for moving goods such as wheat, corn, lumber, coal, and iron ore.
From 1840 to 1844, the population of Buffalo jumped from around 18,000 to just under 30,000. Much of the city was proximate to the harbor. The Buffalo Harbor was becoming overcrowded with ships. Passengers were using steamboats as a mode of travel to cities like Detroit but a ticket would cost 10 dollars.
 A map of Buffalo New York (late 1840s). Credit: buffaloresearch.com
A map of Buffalo New York (late 1840s). Credit: buffaloresearch.com
Before midnight on October 18, 1844, the wind suddenly began to blow from a southwesterly direction and the velocity increased seemingly in an instant. The wind ad rain was relentless! The impending disaster would come from Lake Erie, however. Over the next half hour the whole lower part of Buffalo, south of the Erie Canal became submerged with water from two to eight feet.
On the east side of the city, water came as high as Seneca Street below Michigan Street and completely covered them. The water was rising at by feet per minute! One man who was on Main Street described water as coming up in one huge wave of about four feet in depth. Houses were blown down, roofs were ripped apart and cellars were flooded. The water level on Lake Erie rose an astounding 22 feet! Ships were badly damaged or destroyed all across Lake Erie and debris washed ashore from Buffalo all the way back to Cleveland.
A seawall stone pier of the harbor was breached. Massive boulders weighing many tons were moved from ten to twenty feet. The track of the Attica- Buffalo railroad for a mile and a half was washed up so that cars had to leave from a neighboring town in the afternoon.
According to “A Line From Linda” blog – At Huff’s Hotel, guests were pulled out of their beds and swept into the lake. Two hundred buildings were demolished and debris covered South Buffalo. Two families, stranded on a rooftop of a house, were set adrift when the house broke loose from its foundation. The roof shortly split in two, serving as life rafts until their occupants were rescued.
According to hamburg.wgrz.com The steamboat Robert Fulton, after losing two or three passengers who were washed overboard, was piled upon the sand beach above Sturgeon Point. The steamer G.W. Dale floated across Ohio Street. The Steamer Columbus ended up in a pasture 200 feet from Buffalo Creek!
In the lower districts of the city, there were many harbor craft and canal boats left by the receding waters, many canal boats being out on the commons, on Division, Eagle, and Clinton streets. South Buffalo was strewn with miscellaneous wreckage of all kinds.
It is safe to say that upwards of two hundred small buildings in the lower part of the city were entirely destroyed. There is scarcely a house in its original position on the other side of the Creek. At the corner of Main and Ohio streets, the water was six feet deep and at Michigan and Exchange streets it was five feet deep!
Needless to say, in addition to the loss of life, extensive damage was inflicted by the storm on Buffalo, Harbor. It would take most of the rest of the decade for commerce to return to normal.
All told, the official death toll in Buffalo was 53 while 25 perished on boats that were on Lake Erie. The actual toll was probably much greater (well into three digits). There were reports of bodies found that were swept out of hotels and homes (probably while they were sleeping).
 The photo shows a damaged ship on Lake Erie on October 19, 1844. Credit http://hamburg.wgrz.com.
The photo shows a damaged ship on Lake Erie on October 19, 1844. Credit http://hamburg.wgrz.com.
By the end of the 1840s, Buffalo had recovered from this catastrophic event. The harbor was rebuilt and it was significantly expanded to handle the increased ship traf c as the city became a major hub for shipping along the Great Lakes.
The population grew rapidly around the turn of the century due to immigration and the availability of jobs. According to the 1920 census, just before my mother was born there, Buffalo was the 11th largest city in the U.S. with a population of over 506, 000. The population peaked around the 1950 census at over 580,000. I was born there two years later, about a mile from the high-impact area.
Storm Analysis
Since it was 1844, there were no weather maps for me to refer to, so I had to construct the scenario with the information that I could find. The featured image of this article is my best guess of the surface weather map from this ill-fated day. Since Lake Erie is oriented more or less from the southwest to the northeast, the lower lake level was a product of the prevailing northeast winds in the two days prior to the storm.
The sudden change of the wind to the southwest and the severity of the storm changed all of that in a hurry.
Short-term fluctuations that often occur on the Great Lakes create a storm surge which is known as a seiche. The storm surge is created by high sustained winds from one direction that push the water level up at one end of the lake and makes the level drop by a corresponding amount at the opposite end.
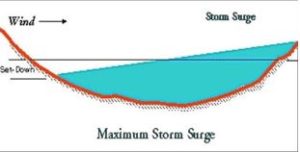 This diagram indicates the mechanisms involved with the development of a storm surge (seiche) on the Great Lakes. Credit- msu.edu.
This diagram indicates the mechanisms involved with the development of a storm surge (seiche) on the Great Lakes. Credit- msu.edu.
From the bits of information that I can gather, it appears that the prevailing northeast wind switched quickly to the southwest and the wind became ferocious in a hurry. By the next day, a northwest wind was reported.
To the north, the barometric pressure at Toronto Ontario bottomed out at 28.85 inches of mercury (or 977 millibars). That would be equivalent to a Category 2 hurricane. Wind gusts exceeding hurricane force were also reported in Toronto.
I suspect that a warm front pushed through Buffalo during the evening as a powerful area of low pressure passed to the north around Toronto. Later, the wind shift to the northwest signified a cold frontal passage. Wind gusts at Buffalo were probably not much lower than in Toronto.
The strong and persistent southwest wind wreaked havoc on Lake Erie and led to the extreme seiche at Buffalo.
 A photo of a Lake Erie (seiche) November 2003 Credit- glerl.noaa,gov
A photo of a Lake Erie (seiche) November 2003 Credit- glerl.noaa,gov
Significant seiche events occur every few years in Buffalo, but they have yet to match this beast of a storm and its associated surge.


